Turmeric - The Amazing Health Benefits
- Lora Leon
- May 20, 2016
- 3 min read

Turmeric is a commonly used spice in Indian and other ethnic cuisines. This herb has also become much more popular in the Western world with frequent use of traditional or alternative medicine practices and natural beauty regimens. Many doctors and patients are looking to traditional and alternative methods to compliment the harsher treatments of modern medicine. The uses for turmeric are never-ending, from beauty purposes to health benefits. Promising studies have displayed the cancer-slowing properties of curcumin (curcuma longa), a strong extract of turmeric, and similar studies have shown turmeric’s antifungal and antibacterial properties. This spice can not only rev up your kitchen, but also your mind, body, and soul. Many women across the world add this spice to their baths for beautiful skin (be careful, it can stain a white tub!) while doctors of Eastern medicine have used this herb to treat patients for thousands and thousands of years.
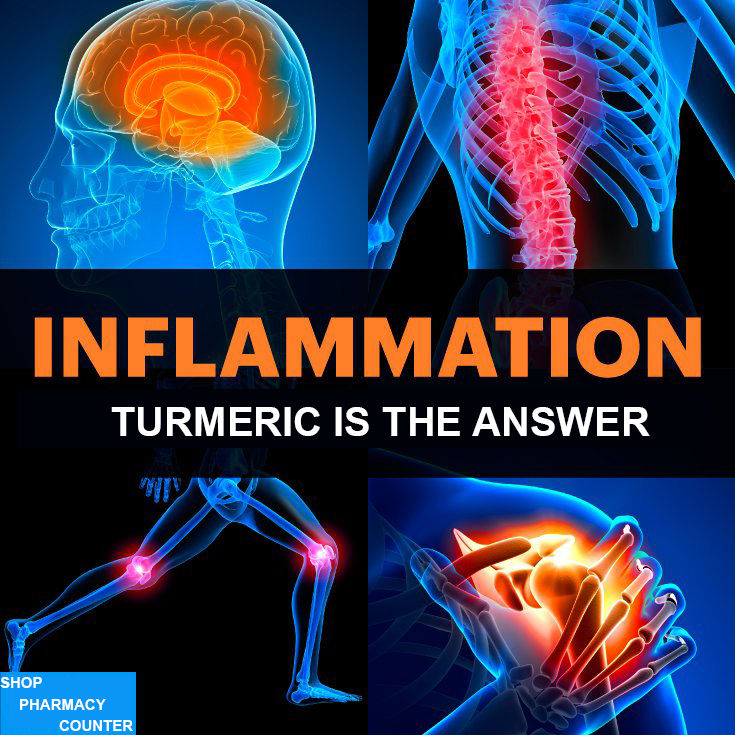
The known health benefits of turmeric seem to be increasing over time with each new study that is done with this amazing herb. The curcumin found in turmeric has been shown to act as an anti-inflammatory agent and has the ability to benefit the human body when dealing with a various number of ailments. Some of the illnesses that have been looked at with turmeric use include neurodegenerative disorders, cardiovascular disease, pulmonary disorders, metabolic issues, as well as autoimmune diseases. Inflammation in the body can be the cause of a various number of health complications. It can affect all systems of the body, affecting a person in many ways, from gut health to joint health to neurological health and everything outlying and in between. Over time, if inflammation is left unchecked and untreated, it has the ability to lead to fatal disease. Turmeric is a safe and natural way to fight inflammation in the body without resorting to OTC anti-inflammatories that can contain harmful ingredients when taken regularly.
Turmeric with Bioperine to Fight Inflammation
Bioperine is an extract from black pepper that

has been shown to aid the body in its absorption of turmeric, enhancing the health benefits of this remarkable herb. Turmeric, itself, has not shown toxicity levels in studies with rats, so you can feel safe adding turmeric with bioperine to your daily dietary supplements. In this toxicity study, the rats receiving the turmeric also had a lower body weight than the control group, so could it be that turmeric may also help with weight loss? Perhaps over time, more studies will show the ability of turmeric to aid in weight loss. However, black pepper has been shown to help study participants shed some excess weight, so it is easy to see how this combination of turmeric and bioperine can help with a wide variety of health issues from cancer prevention to obesity, while also fighting off harmful inflammation in the body.
Click here to purchase your own turmeric organic complex w/ bioperine from Potent Supplements LLC, your new spot for all natural supplements. Stop on in to our online store to buy some organic turmeric with bioperine and experience all the incredible health benefits for yourself. While you’re there, take some time to check out our blog and read about how others have used natural supplements to enhance their overall well-being.
References Aggarwal, B. B., & Harikumar, K. B. (2009). Potential therapeutic effects of curcumin, the anti-inflammatory agent, against neurodegenerative, cardiovascular, pulmonary, metabolic, autoimmune and neoplastic diseases. The international journal of biochemistry & cell biology, 41(1), 40-59. Retrieved from http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1357272508002550
Apisariyakul, A., Vanittanakom, N., & Buddhasukh, D. (1995). Antifungal activity of turmeric oil extracted from Curcuma longa (Zingiberaceae). Journal of ethnopharmacology, 49(3), 163-169. Retrieved from http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0378874195013202
Kuttan, R., Bhanumathy, P., Nirmala, K., & George, M. C. (1985). Potential anticancer activity of turmeric (Curcuma longa). Cancer letters, 29(2), 197-202. Retrieved from http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0304383585901594
National Toxicology Program. (1993). NTP Toxicology and Carcinogenesis Studies of Turmeric Oleoresin (CAS No. 8024-37-1)(Major Component 79%-85% Curcumin, CAS No. 458-37-7) in F344/N Rats and B6C3F1 Mice (Feed Studies). National Toxicology Program technical report series, 427, 1. Retrieved from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?Cmd=ShowDetailView&Db=pubmed&TermToSearch=12616304&itool=EntrezSystem2.PEntrez.Pubmed.Pubmed_ResultsPanel.Pubmed_RVAbstractPlus&ordinalpos=1
Negi, P. S., Jayaprakasha, G. K., Jagan Mohan Rao, L., & Sakariah, K. K. (1999). Antibacterial activity of turmeric oil: a byproduct from curcumin manufacture. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 47(10), 4297-4300. Retrieved from http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/jf990308d
Westerterp-Plantenga, M., Diepvens, K., Joosen, A. M., Bérubé-Parent, S., & Tremblay, A. (2006). Metabolic effects of spices, teas, and caffeine. Physiology & Behavior, 89(1), 85-91. Retrieved from http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0031938406000540




















Comments